Partial Discharge Testing (PD Testing)
-
28 July 2021
Partial discharge testing, also known as PD testing, is performed to assess electrical insulation health. PD is best described as a failure of part of an insulation system to withstand the electrical field applied to it. This can be a result of poor design, poor workmanship, defective materials, contamination, or aging. For decades it has been recognized that partial discharge testing is an excellent method for determining electrical asset health.
Online non-invasive and non-destructive techniques for monitoring and surveying have been proven to provide the necessary level of detail for condition assessment without impacting system operation. We'll discuss it further in this article.
Techniques exist now to test assets from 3KV to 700KV and beyond. Metal clad switchgear and buss work, GIS switchgear and busses, air insulated assets (insulators, arrestors, bushings, etc.), as well as paper insulated and extruded cables can all be tested online without an outage.
What is Partial Discharge?
Before we discuss PD Testing, let’s see and hear (turn up your audio) partial discharge in this short video. Then, we’ll look at defining and testing for PD.
5 min video with Partial Discharge Examples
(turn up your audio. opens on another tab)
Partial Discharge is a flashover of part of the insulation system due to a localized electric field greater than the dielectric withstand capability of that part where the overall insulation system remains capable of withstanding the applied electrical field.
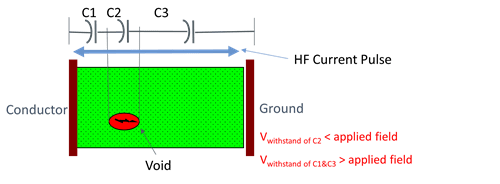
One effect of this flashover is a high frequency current pulse that travels through the capacitance of the insulation (C1 & C3). This current pulse is low energy due to its short (microsecond) duration, but it can negatively affect the insulation and eventually cause catastrophic failure.
What are the Products of Partial Discharge?
Partial discharge breakdown of insulation produces: Light, Heat, Smell, Sound, Electromagnetic Waves, and HF Electric Current.
Where can Partial Discharge Occur?
-Any insulation (Air, Oil, Solid, GIS)
-Wide range of voltages (3kV to 769kV and beyond)
-Indoor and Outdoor Metal clad switchgear cubicles
-Indoor and Outdoor Insulators
-Transformer Cable Boxes
-MV /HV Cables
-Transformers
-SF6 GIS / Oil Filled / Air Insulated
What are the Types of Partial Discharge?
-Surface PD Discharge occurring across the insulation surface, which is the most common form of PD. Surface partial discharge is affected by salt air and humidity.
-Internal PD Discharges occurring in defects, voids, or cavities within solid insulation.
-Corona PD Discharges occurring in gaseous dielectrics in the presence of inhomogeneous fields. Corona partial discharge from the conductor directly into the air and is most commonly found in outdoor electrical assets.
What online partial discharge testing techniques are available?

When detecting PD in MV/HV switchgear, bus ducts, cables, etc. it is much easier if we can do this live without interfering with supply. The most practical ways revolve around detecting different frequency signals. Using a combination of sensors ensures different types of PD can be readily identified.
-Ultrasonic methods are particularly effective at finding surface PD and corona PD. Acoustic emissions from PD activity are normally at a frequency too high for the human ear, i.e. ultrasonic. As the PD gets worse, the frequency sometimes decreases into the audible range. Using an airborne ultrasonic microphone is the most sensitive way to detect PD where there is an air path between the source and the microphone. Contact ultrasonic sensors can be used for sealed chambers.
-PD generates Transient Earth Voltages (TEV) – high frequency electromagnetic pulses. TEV methods are particularly effective at finding internal PD. TEV signals travel across the inside surfaces of switchgear, escaping to the outside through openings in the metalwork e.g. gaskets. PD activity can be detected by placing a TEV sensor on the outside of the switchgear to measure these pulses.
-UHF is ideal as a non-contact detection method for electromagnetic PD signals in open terminal switchyards, cable systems and distribution networks
-HFCT/RFCT Online cable testing can be done using high frequency current transformers (HFCT) or radio frequency current transformers (RFCT) based test systems that measure PD pulses that work their way onto an external cable ground. The advantage is that the cable can be kept in service and the test is quick and very few resources as a offline test would require.
Learn more about Partial Discharge Testing and Monitoring and how it can be a great addition to your preventative maintenance/reliability program. Request a free demo.